Will Quantum Tech Replace Classical Computing? A Deep Dive
Will quantum tech replace classical computing? It’s a question buzzing in tech circles as quantum computers make headlines with breakthroughs like Google’s Willow chip. Unlike classical computers that use binary bits (0s and 1s), quantum tech leverages qubits and quantum mechanics to solve complex problems at unprecedented speeds. This guide explores whether quantum tech will overtake classical systems, their strengths, and what the future holds—perfect for tech enthusiasts and curious beginners alike.
Understanding Quantum Tech vs. Classical Computing
Will quantum tech replace classical computing? To answer, let’s compare the two. Classical computers, like your laptop or smartphone, use bits (0 or 1) to process data sequentially. Quantum computers, however, use qubits that can exist in multiple states simultaneously via superposition and entanglement, enabling parallel computations.
Key Differences:
- Processing Power: Classical computers excel at linear tasks; quantum tech tackles exponential problems like molecular simulations.
- Speed: Quantum computers can solve specific tasks (e.g., factoring large numbers) exponentially faster.
- Stability: Classical systems are reliable; quantum systems are error-prone due to environmental noise.
For example, Google’s Willow chip (2024) solved a problem in 5 minutes that would take a supercomputer 10 septillion years, showcasing quantum’s potential.

Strengths and Limits of Quantum Tech
Will quantum tech replace classical computing entirely? Not likely, as each has unique strengths.
Quantum Tech Strengths:
- Complex Simulations: Ideal for drug discovery, like simulating molecular interactions for new medicines.
- Optimization: Solves logistics problems, such as optimizing supply chains for companies like Amazon.
- Cryptography: Can break traditional encryption, driving quantum-safe solutions.
Quantum Tech Limits:
- Error Rates: Qubits are sensitive to noise, requiring advanced error correction (e.g., Google’s 2025 breakthroughs).
- Cost: Quantum systems are expensive, limiting access to tech giants and research labs.
- General Tasks: Classical computers are better for routine tasks like browsing or word processing.
Outbound Link: Google’s Quantum Advancements for details on error correction breakthroughs.
Why Classical Computing Still Matters
Will quantum tech replace classical computing in practical applications? Classical systems remain essential for most computing needs. Your smartphone, cloud servers, and even supercomputers rely on classical architecture for reliability and versatility.
Why Classical Computing Endures:
- Mature Technology: Decades of development make classical systems stable and affordable.
- Broad Applications: From gaming to data storage, classical computers handle diverse tasks efficiently.
- Infrastructure: Global IT systems are built on classical frameworks, making a full switch impractical.
For instance, IBM’s hybrid quantum-classical systems integrate quantum for specific tasks (e.g., optimization) while classical systems handle data processing, showing coexistence is key.
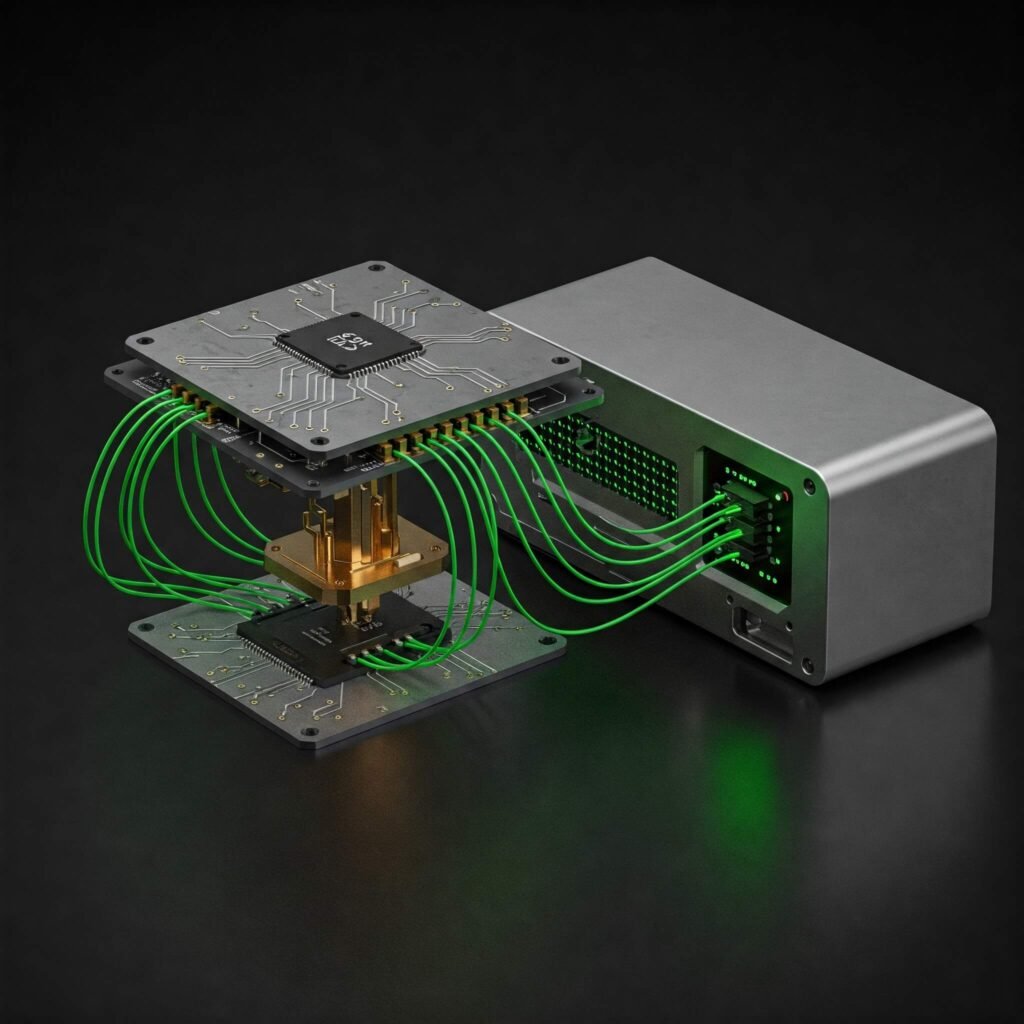

The Rise of Hybrid Computing
Will quantum tech replace classical computing, or will they merge? The future points to hybrid computing, where quantum and classical systems work together. This approach leverages quantum’s power for specialized tasks and classical reliability for general computing.
Benefits of Hybrid Computing:
- Efficiency: Quantum handles complex calculations; classical manages routine tasks.
- Scalability: Hybrid systems are more practical than fully quantum ones, given current limitations.
- Accessibility: Companies like IBM and Microsoft offer cloud-based quantum-classical platforms, democratizing access.
For example, JPMorgan Chase uses IBM’s Qiskit to run quantum algorithms for financial modeling on classical infrastructure, achieving faster results without replacing existing systems.
Outbound Link: IBM’s Hybrid Computing Solutions for insights into integration.
What the Future Holds for Quantum Tech
Will quantum tech replace classical computing in the long term? Experts predict a collaborative future. By 2030, quantum tech could generate $1.88 billion, with applications in healthcare, finance, and climate science, according to McKinsey. However, classical computing will remain the backbone of everyday tech.
Future Trends:
- Quantum Advantage: Quantum systems will dominate niche areas like cryptography and AI training.
- Error Correction: Advances (e.g., Microsoft’s Majorana chip) will make quantum tech more reliable.
- Quantum Networking: Cisco’s 2025 quantum networking chip enables instant quantum communication, enhancing hybrid systems.
Challenges like cybersecurity risks (e.g., quantum breaking encryption) are driving quantum-safe cryptography development, ensuring classical systems stay secure.
How to Prepare for the Quantum Tech Era
Will quantum tech replace classical computing in your lifetime? While it won’t fully replace classical systems, quantum tech will shape industries. Here’s how to stay ahead:
Actionable Steps:
- Learn Quantum Basics: Take free courses on edX or Qiskit.
- Experiment: Use IBM’s Qiskit or Microsoft’s Quantum Development Kit to explore quantum programming.
- Stay Informed: Follow tech news on X or blogs from IBM, Google, and D-Wave.
- Assess Impact: Businesses should evaluate quantum’s potential for their industry, like finance or healthcare.
Outbound Link: McKinsey’s Quantum Report for economic forecasts.
Conclusion: Will Quantum Tech Replace Classical Computing?
Will quantum tech replace classical computing? The answer is no—but it will transform computing by complementing classical systems. Quantum tech excels in specialized tasks, while classical computing remains essential for everyday needs. Hybrid systems are the future, blending the best of both worlds. Start exploring quantum tech today to stay ahead in this exciting era.



































